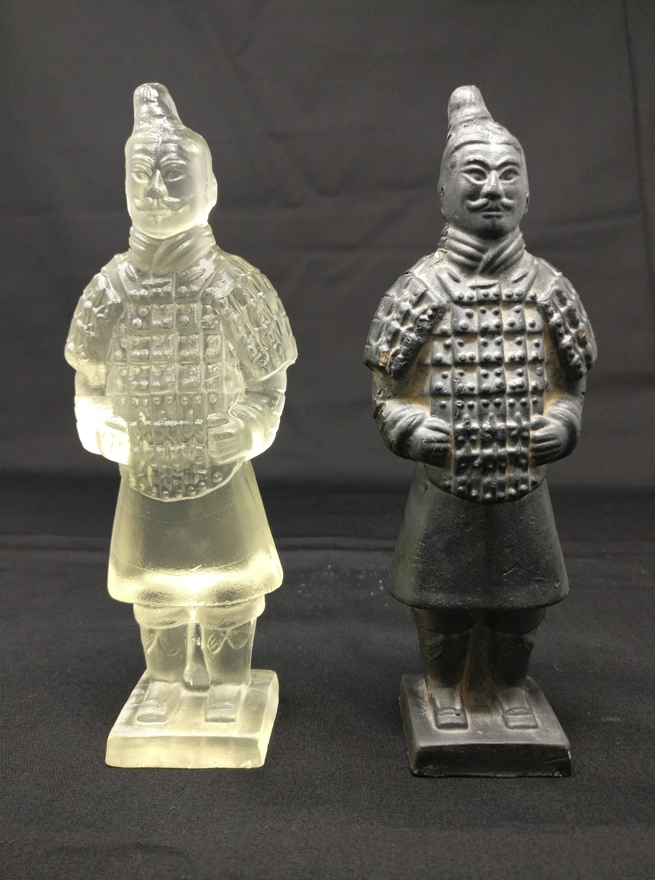
The Basics: Reverse Engineering
The art of creating a second copy of an original object
In the manufacturing industry, time is everything. If you have a product item, it can be prohibitively expensive to produce dozens of prototypes through traditional injection moulding techniques. That’s where reverse engineering and rapid prototyping come in. Thanks to state-of-the-art laser scanners and software, OR3D can take an item and scan it to produce a 3D model, which can then be 3D printed incredibly accurately.
What is Laser Scanning?
Laser scanning is the process of using a laser to scan an object and capture its shape and features in a 3D digital format. The scanner emits a laser beam that moves across the surface of the object and measures the distance to the object at each point. This data is then used to create a 3D digital model of the object (usually as an STL file). Laser scanning can be done with different levels of accuracy and resolution depending on the desired outcome and what is needed by the end user. Once the laser scan is complete and the 3D model is created, the next step is to use 3D printing to create a physical replica of the scanned object.
What is 3D Printing?
For more information on 3D printing, you should visit our article on it here, but in layman’s terms 3D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding layers of material, such as plastic or metal, until the object is complete. The 3D printer reads the digital model created by the laser scan and uses it as a guide to create the physical replica of the object.
What are the Benefits of Reverse Engineering?
There are multiple benefits to reverse engineering an object in this way. The process allows for accurate replication of objects, including those with intricate details that would be difficult to reproduce by hand or slow to reproduce via other methods like injection moulding. It also allows for the creation of multiple copies of an object, which can be useful for applications such as product design and manufacturing.
Reverse engineering can also be used for the restoration of historical artefacts. By laser scanning and 3D printing a replica of an artefact, it is possible to study and analyse it without risking damage to the original. Additionally, the replica can be used for public displays, educational purposes, or even to replace missing pieces of the original artefact.
In Conclusion
As the price of hardware like 3D printers and laser scanners comes down, this technology is becoming more affordable for more and more people, and it’s already changed the way we design and manufacture things for the better.
If you have an item you need reverse engineering, consider getting in touch with OR3D today at:
Phone – 01691 777774
email – info@or3d.co.uk
Our Contact page – https://www.or3d.co.uk/contact-us/