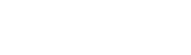Nominal Actual Comparison
What is a Nominal Actual Comparison?
A nominal actual comparison, sometimes referred to as a 3D compare, is a way of showing and analysing the differences between a reference and a measured object.
Visualising a Nominal Actual Comparison
Most commonly a 3D compare is displayed as a colour map where the colours represent the magnitude of deviation between the reference and measured objects. A colour scale between red and blue is usually used where green lies in the middle identifying areas where there is minimal deviation.
The comparison can also be visualised in 2D where a coloured whisker plot is used.
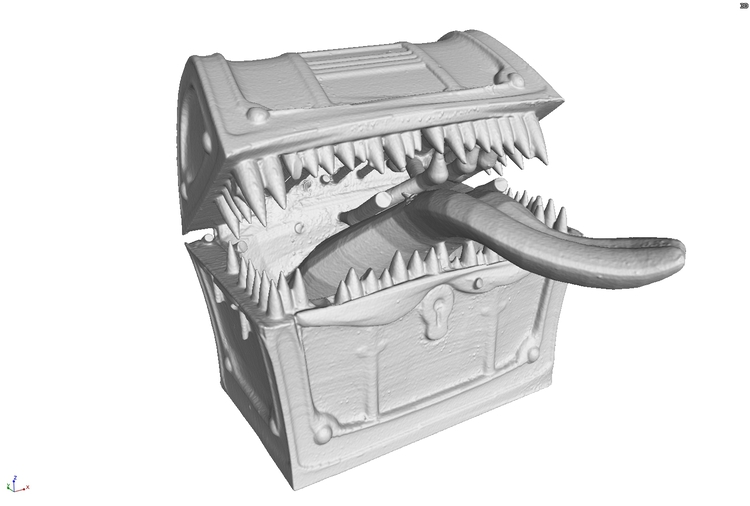
Analytical Information
As well as the colour map which visualises the deviation, a histogram is typically produced showing the spread of deviation values. As well as this, tags can be generated at user definable locations to give accurate measurements of deviation at those points.
Further Analysis
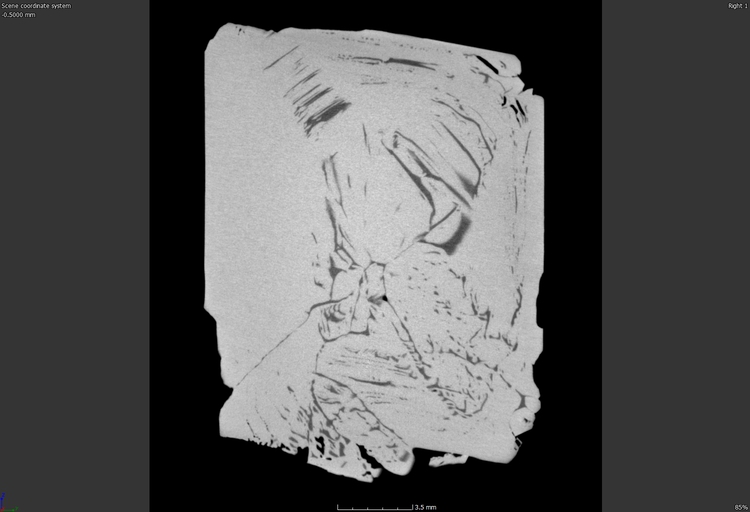
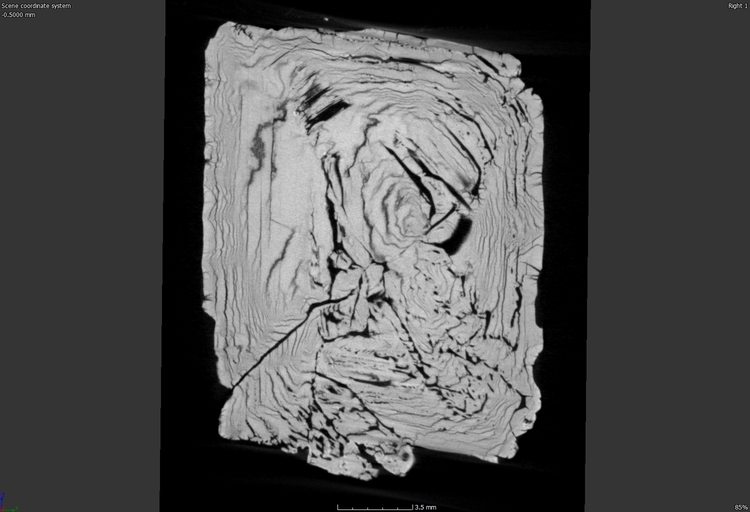
It can also be interesting to visualise the deterioration of parts over time due to different factors. The images below show the difference before and after the dehydration of a mineral.